Transdisciplinary Science and Engineering News
Labs spotlight #5 - Sato Yuriko Lab. -
Cross-border Human Mobility and Multicultural Synergy
This "Spotlight" series features a laboratory from the Department and introduces you to the laboratory's research projects and outcomes. This time we focus on Sato Yuriko Laboratory.

Global Engineering for Development, Environment and Society
Laboratory : Room 206, West Bldg.1, O-okayama campus
Associate Professor Yuriko Sato![]()
Member : Doctor students 2, Master students 10, Undergraduate students 2, Special Researchers 2
| Areas of Research | International Student Policy / Immigration Policy / International Education / Development Economics |
|---|---|
| Keywords | International Students / Highly Skilled / International Education / Multicultural Synergy |
| Website | Yuriko Sato Laboratory |
Summary

Globalization has promoted cross boarder human mobility.
We need to realize social environment in which people from different cultural background work together and create multicultural synergy.
International students are key actors in such environment.
We study on the determinants of international student mobility and their roles in workplaces and communities.
Research interests
What determines international students’ choices of study destination and workplace?
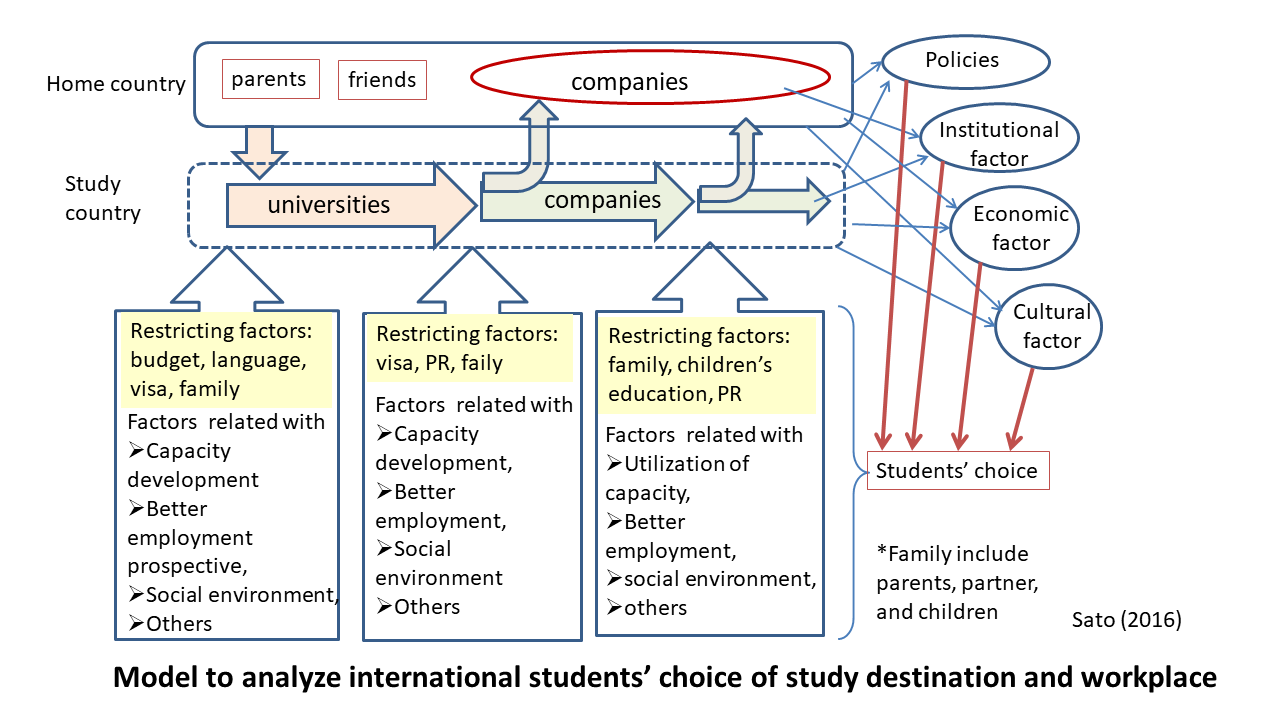
International students make important decisions in choosing study destination, workplace and place of settlement. The figure shows a model to analyze the factors which influence their decisions. This model assumes that they consider restricting factors (budget, language, visa, family intention) first, then choose the country/place which will satisfy the other factors (advancement of ability and skills, better employment & social environment etc.) according to their priorities. Decision will also be influenced by policies and economic, institutional and cultural factors of their home country and destination country.
| Source: | Sato, Yuriko (2016)“Characteristics and Issues of Brain Circulation of International Students: From an Analysis of Influencing Factors on International Students’ Choices in Germany and Implications for Japan” |
Advantage in Student Recruitment and Cost of International Education
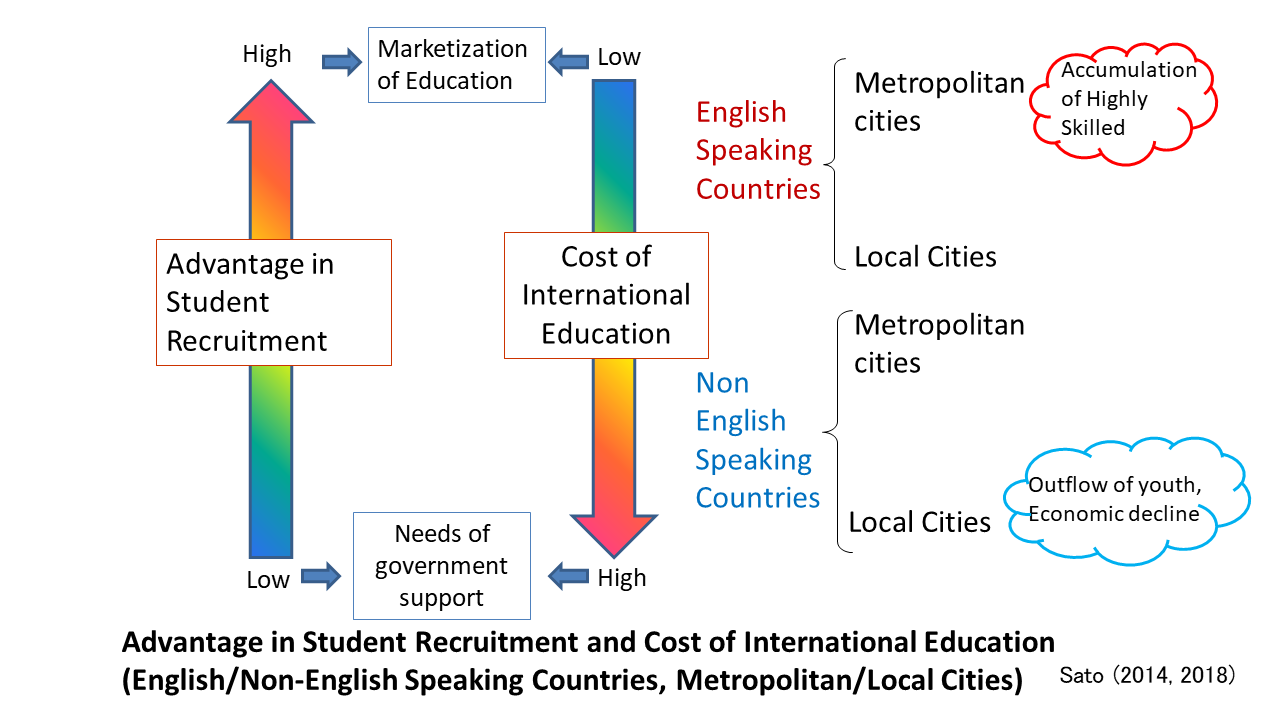
Since English is most commonly used language in the world and English proficiency is highly evaluated in labor market, English speaking countries have advantage in recruitment of international students as shown in the figure.
Cost of international education tend to be lower in English speaking countries than non-English speaking countries where the universities often need to bear the cost of local language courses, courses taught in English and support desk.
Metropolitan cities have advantage in recruitment of international students than local cities since many students prefer to study in Metropolitan cities where they can find more information, employment opportunities and stimulation.
Cost of international education in local cities in non-English speaking countries tend to be higher than metropolis since they have much less facilities to support foreigners. Consequently, the big cities in English speaking countries tend to attract the highly skilled which lead to the prosperity in knowledge-based economy while the local cities in non-English speaking countries tend to face the outflow of the youth and economic decline.
| Source : | Sato, Yuriko (2014) ”Measures to Reduce the Gap Between the Metropolitan Area and Other Regions in the Internationalization of Education: From the Comparison of Korea and Japan” |
| Sato, Yuriko (2018) “Cost Sharing of International Student Recruitment and Support at Local Private Universities in Korea and Japan” |
Publication list
Representative paper
- [1]Sato, Yuriko (2018) International Student Policy as de facto Entry Point of Immigration and Refugee Policy in Japan: Merits and Problems of Versatile International Student Policy"
 , Migration Policy Review, Vol. 10, pp. 29-43
, Migration Policy Review, Vol. 10, pp. 29-43 - [2]Sato, Yuriko (2019) “Asian Students’ Brain Circulation and Japanese Companies: An empirical study to explore the relationship”, Asian Education and Development Studies, Vol. 9, No.1, pp. 105-116, Article DOI: 10.1108/AEDS-02-2019-0044

Major Publications
- [1]Sato, Yuriko (2010)"Evaluation of Japan's Foreign Student Policy: From the Perspective of Human Resource Development, Friendship Promotion and Economic Effect", Toshindou, pp. 1-238
- [2]Sato, Yuriko (2020)"Chapter 3: Policy to Attract the Highly Skilled and International Students" in "Interactive Seminar:Co-Creation through Multicultural Synergy", Tokai University Publication
About researcher and lab
- From Associate Professor Yuriko Sato
- In Sato lab, students from various countries work together using various disciplines, which, we hope, will lead to multicultural and interdisciplinary synergy!
- Faculty and Research Laboratories
- Tokyo Tech Indonesia Commitment Awards 2019 held|Tokyo Tech News
- Indonesian Student Association holds career seminar | Tokyo Tech News
Contact
Associate Professor Yuriko Sato
E-mail yusato@ tse.ens.titech.ac.jp
*Find more about the lab and the latest activities at the lab site![]() .
.