Chemical Science and Engineering News
From Defects to Order: Spontaneously Emerging Crystal Arrangements in Perovskite Halides
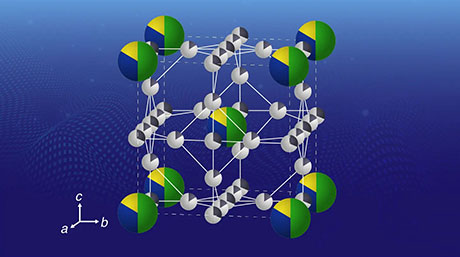
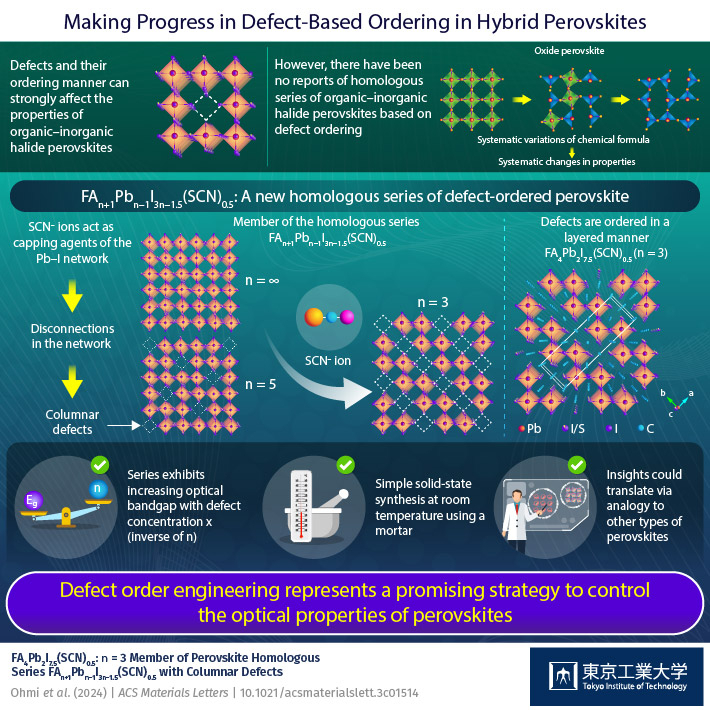
A new hybrid layered perovskite featuring elusive spontaneous defect ordering has been found, report scientists at Tokyo Tech. By introducing specific concentrations of thiocyanate ions into FAPbI3 (FA = formamidinium), they observed that ordered columnar defects appeared in the stacked crystalline layers, taking up one-third of the lattice space. These findings could pave the way to an innovative strategy for adjusting the properties of hybrid perovskites, leading to practical advances in optoelectronics and energy generation.
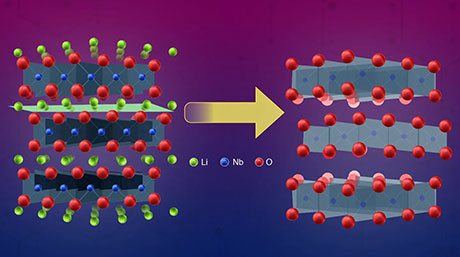
Perovskites are among the most extensively studied materials in modern materials science. Their often unique and exotic properties, which stem from perovskite's peculiar crystal structure, could find revolutionary applications in various cutting-edge fields. One intriguing way of realizing such properties is through the precise ordering of a perovskite's defects, such as vacancies or substitutions.
In oxide chemistry, scientists have known for a long time that oxide defects can spontaneously and consistently arrange themselves throughout the crystal lattice, once they reach certain concentrations (e.g. integer ratio). This emerging order can give rise to attractive properties. While defect ordering has been observed numerous times in perovskite oxides, the same cannot be said about hybrid halide perovskites, composed of an organic cation, a metal cation, and a halide anion.
Interestingly, in a recent study published in ACS Materials Letters![]() , a research team including Associate Professor Takafumi Yamamoto from Tokyo Institute of Technology discovered a new defect-ordered layered halide perovskite, shedding light on how order can emerge through defects in these compounds. This work was inspired by a previous finding reported by the researchers, namely the formation of 'defect columns' obtained by introducing thiocyanate ion (SCN−) into the crystal lattice of FAPbI3 to obtain FA6Pb4I13.5(SCN)0.5. "We hypothesized that, if the concentration of SCN in the lattice increased, the amount of the PbI columnar defects would also increase, leading to different types of defect ordering, as seen in vacancy-ordered perovskite oxides," explains Dr. Yamamoto.
, a research team including Associate Professor Takafumi Yamamoto from Tokyo Institute of Technology discovered a new defect-ordered layered halide perovskite, shedding light on how order can emerge through defects in these compounds. This work was inspired by a previous finding reported by the researchers, namely the formation of 'defect columns' obtained by introducing thiocyanate ion (SCN−) into the crystal lattice of FAPbI3 to obtain FA6Pb4I13.5(SCN)0.5. "We hypothesized that, if the concentration of SCN in the lattice increased, the amount of the PbI columnar defects would also increase, leading to different types of defect ordering, as seen in vacancy-ordered perovskite oxides," explains Dr. Yamamoto.
The team synthesized FAPbI3 perovskite powders and single crystals via solid-state reactions using precisely defined concentrations of starting materials, including specific ratios of SCN−. They found that when an appropriately high ratio of SCN− was used, the obtained perovskite was represented by the formula FA4Pb2I7.5(SCN)0.5. This layered compound, like the previously reported one, also exhibited columnar defects spanning all stacked layers. However, unlike FA6Pb4I13.5(SCN)0.5, in which one-fifth of the PbI columns were orderly defected, one-third of all columns in the new FA4Pb2I7.5(SCN)0.5 were defects.
The main novelty of this discovery is that the new compound, alongside the previous one, forms what's known as a 'homologous series.' This means that systematic variations of the compound's chemical formula, which can be represented using integer variables, result in systematic changes in its properties. In this case, the researchers found that the optical bandgap of the material increased with the concentration of ordered defects in the lattice.
Worth noting, this work presents the first homologous series based on defect ordering found for hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites. "This study provides a new playground for defect engineering in organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite compounds. We believe that this new field has the potential to develop by an analogy to the defect-ordering already seen in perovskite oxides," remarks Dr. Yamamoto. "We have also provided a new strategy to control the defect orderings for tuning a perovskite's optical properties by incorporating SCN−."
With any luck, these findings will translate to progress in an exciting area of materials science, ultimately leading to new perovskites with useful qualities for next-generation technologies.
- Reference
| Authors : | Takuya Ohmi1, James R. Neilson2, Wataru Taniguchi1, Tomoya Fukui3, Teppei Nagase1, Yuki Haruta4, Makhsud I. Saidaminov4, Takanori Fukushima3,5, Masaki Azuma1,5,6, and Takafumi Yamamoto1,* |
|---|---|
| Title : | FA4Pb2I7.5(SCN)0.5: n = 3 Member of Perovskite Homologous Series FAn+1Pbn−1I3n−1.5(SCN)0.5 with Columnar Defects |
| Journal : | ACS Materials Letters |
| DOI : | 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.3c01514 |
| Affiliations : |
1 Laboratory for Materials and Structures, Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2 Department of Chemistry, Colorado State University, United States 3 Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science, Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 4 Department of Chemistry, University of Victoria, Canada 5 Living Systems Materialogy (LiSM Research Group), International Research Frontiers Initiative (IRFI), Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 6 Kanagawa Institute of Industrial Science and Technology, Japan |
|
* Corresponding author's email: yama@msl.titech.ac.jp |
|
- Isomerism Can Control and Increase the Diversity of Structure of Covalent Organic Frameworks, Emerging Nanoporous Solids | Tokyo Tech News
- New Insight for Stabilizing Halide Perovskite via Thiocyanate Substitution | Tokyo Tech News
- A High-Pressure Flux Method to Synthesize High-Purity Oxyhydrides | Tokyo Tech News
- Advanced X-Ray Technique Unveils Fast Solid-Gas Chemical Reaction Pathways | Tokyo Tech News
- Towards More Efficient and Eco-Friendly Thermoelectric Oxides with Hydrogen Substitution | Tokyo Tech News
- Visualizing Temperature Transport: An Unexpected Technique for Nanoscale Characterization | Tokyo Tech News
- Can a flowing liquid-like material maintain its structural order like crystals? | Tokyo Tech News
- No Assembly Required: Self-assembling Silicone-based Polymers | Tokyo Tech News
- Takafumi Yamamoto | Researcher Finder - Tokyo Tech STAR Search
- Masaki Azuma | Researcher Finder - Tokyo Tech STAR Search
- Tomoya Fukui | Researcher Finder - Tokyo Tech STAR Search
- Takanori Fukushima | Researcher Finder - Tokyo Tech STAR Search
- Azuma and Yamamoto Laboratory
- Fukushima Laboratory
- Laboratory for Materials and Structures
- Research Center for Autonomous Systems Materialogy (ASMat)
- Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science
- Institute of Innovative Research (IIR)
- Department of Materials Science and Engineering, School of Materials and Chemical Technology
- Chemical Science and Engineering Graduate Major|Education|Department of Chemical Science and Engineering, School of Materials and Chemical Technology
- Chemical Science and Engineering Undergraduate Major|Education|Department of Chemical Science and Engineering, School of Materials and Chemical Technologyy
- Colorado State University
- University of Victoria
- Latest Research News
School of Materials and Chemical Technology
—Encompassing the Disciplines of Science—
Information on School of Materials and Chemical Technology inaugurated in April 2016
Further Information
Associate Professor Takafumi Yamamoto
Institute of Innovative Research,
Tokyo Institute of Technology
Email yama@msl.titech.ac.jp