Computer Science News
Discovering potential therapeutic protein inhibitors for Chagas disease through computational drug discovery and in vitro enzyme assays
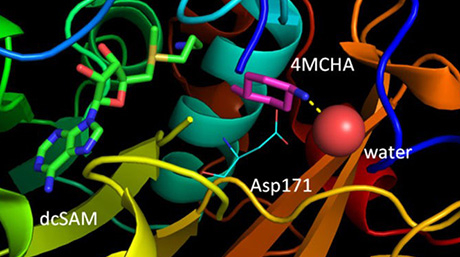
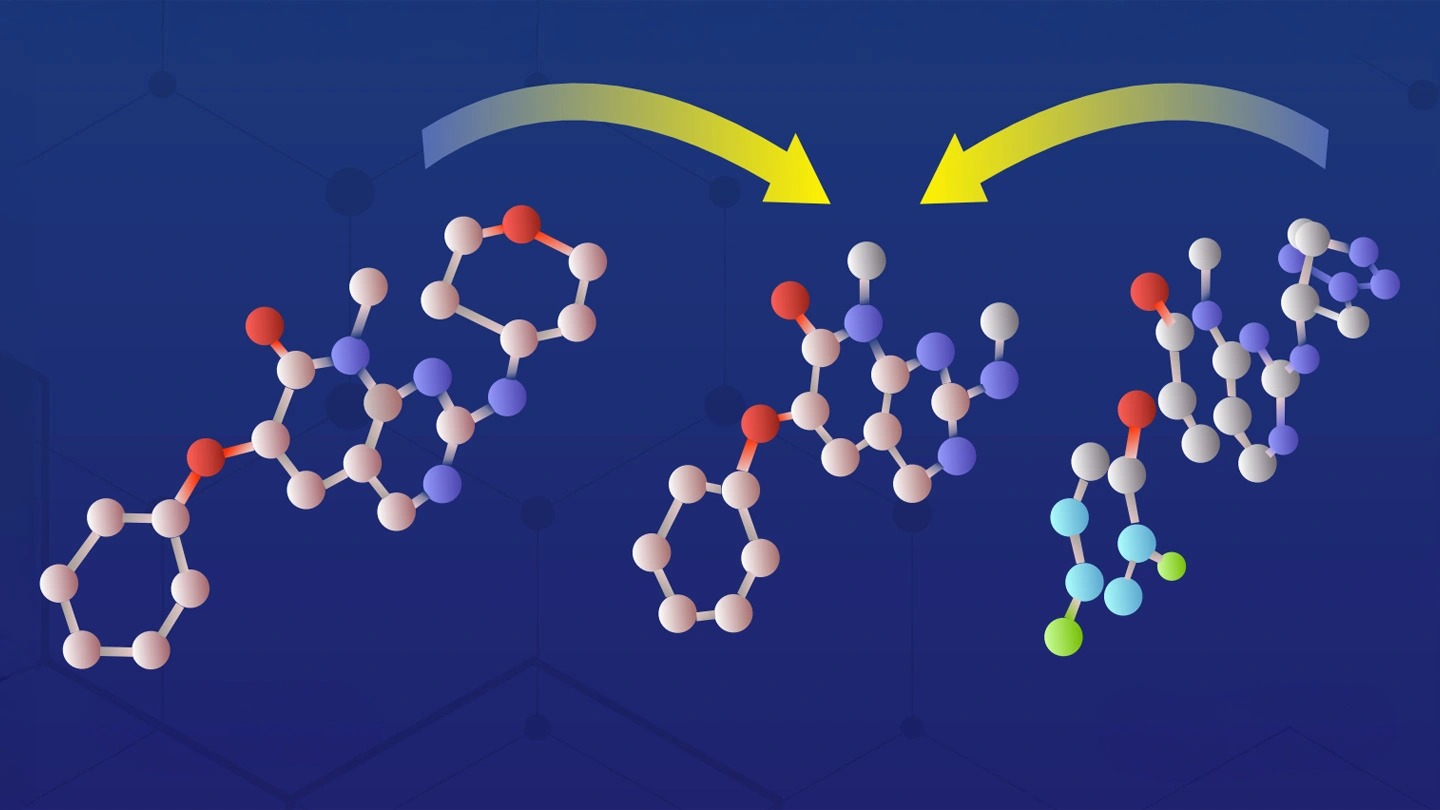
Scientists at Tokyo Tech, Nagasaki University have identified four potential protein inhibitors and unlocked drug discovery strategies for the treatment of Chagas disease by using advanced three-dimensional computer simulation by supercomputer TSUBAME in combination with in vitro experiments and X-ray crystallography. Through this "smart drug discovery" in which IT drug discovery and biochemical experiments cooperate, they identified hit compounds for target protein with a hit rate of 20 times or more than conventional High Throughput Screening (HTS) methods.
Reference
Authors :
Ryunosuke Yoshino3,4,6, Nobuaki Yasuo2,6, Yohsuke Hagiwara2,5, Takashi Ishida1,2,6, Daniel Ken Inaoka7,8, Yasushi Amano5, Yukihiro Tateishi5, Kazuki Ohno2,5,9, Ichiji Namatame5, Tatsuya Niimi5, Masaya Orita5, Kiyoshi Kita7,8, Yutaka Akiyama1,2,6 , and Masakazu Sekijima1,2,3,6
Title of original paper :
In silico, in vitro, X-ray crystallography, and integrated strategies for discovering spermidine synthase inhibitors for Chagas disease
Journal : Scientific Reports
DOI : 10.1038/s41598-017-06411-9 outer
Affiliations :
1 Advanced Drug Discovery Unit, Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology
2 Education Academy of Computational Life Sciences (ACLS), Tokyo Institute of Technology
3 Global Scientific Information and Computing Center, Tokyo Institute of Technology
4 Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences, The University of Tokyo
5 Medicinal Chemistry Research Labs, Drug Discovery Research, Astellas Pharma Inc.
6 Department of Computer Science, Graduate School of Information Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology
7 Department of Biomedical Chemistry, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo
8 School of Tropical Medicine and Global Health, Nagasaki University