Life Science and Technology News
Unraveling the Role of ADGRF5: Insights into Kidney Health and Function
Scientists revealed the role of endothelial cell receptor in maintaining the integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier
The absence of Adhesion G-protein-coupled receptor F5 (ADGRF5) led to significant changes in gene expression in glomerular endothelial cells, disrupting the structure and function of the glomerular filtration barrier, as discovered by researchers from Tokyo Tech and Kyorin University. Their study, employing genetic knockout and knockdown techniques in mice and human cells, elucidates ADGRF5's crucial role in barrier maintenance and proposes potential therapeutic approaches for glomerular diseases.
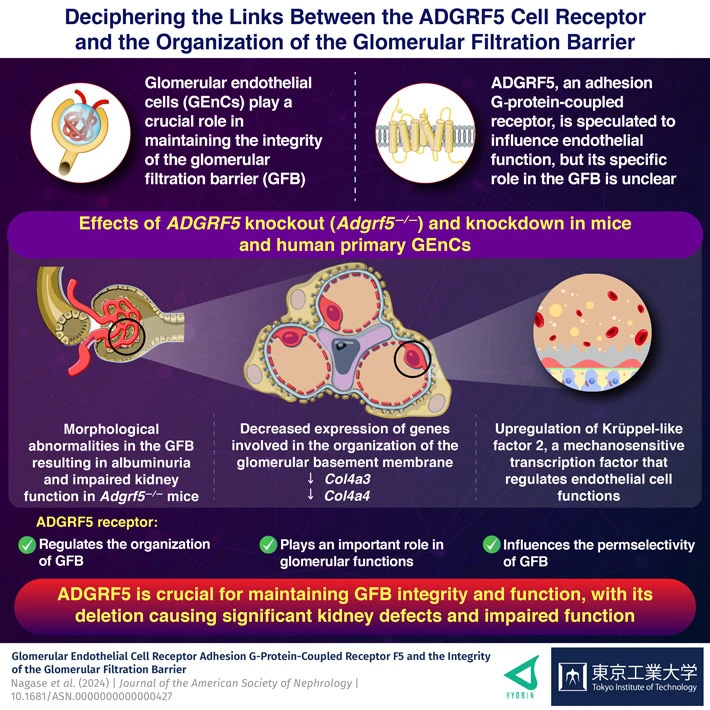
Glomerulus, the fundamental filtering unit of the kidney, is an intricate network of capillaries — small blood vessels that regulate the movement of ions, water, and metabolites while maintaining impermeability to essential macromolecules such as proteins. The selectively permeable capillary wall, known as the glomerular filtration barrier (GFB), consists of three main components: glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs), the glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes. GEnCs line the inner surface of the capillary wall and are covered by a thin layer of glycoproteins and other carbohydrate-based moieties.
Adhesion G-protein-coupled receptor F5 (ADGRF5), a transmembrane cell receptor expressed in GEnCs, is implicated in influencing the integrity of the GFB, potentially playing a role in its structural and functional maintenance. To elucidate the precise role of ADGRF5 in maintaining the integrity of the GFB, a collaborative research study was undertaken by scientists from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) and Kyorin University. Their findings were published in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology![]() on June 06, 2024.
on June 06, 2024.
The research team led by Associate Professor Nobuhiro Nakamura from the School of Life Science and Technology, Tokyo Tech, Japan, and Professor Miki Nagase from the Department of Anatomy, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Japan, conducted a series of genetic knockout and knockdown experiments in mice and human primary GEnCs to investigate the specific role and underlying mechanisms of ADGRF5 in maintaining the GFB.
Explaining the motivation behind the present research, Dr. Nakamura shares "During our analysis of renal gene expression profiles using the Nephroseq v5 database, we observed a reduced expression of ADGRF5 mRNA in the glomeruli of patients with diabetic nephropathy. Additionally, there was a positive correlation between glomerular ADGRF5 expression and the estimated glomerular filtration rate."
Initially, the researchers observed the specific expression of ADGRF5 within endothelial cells that line the glomerular capillary wall. In mice with genetic knockout of ADGRF5, the GFB was affected by morphological abnormalities like splitting and thickening of the glomerular basement membrane and GEnC detachment. The overall integrity of GFB was severely impacted leading to albuminuria - presence of albumin proteins in urine.
Furthermore, deletion and knockdown of the ADGRF5 gene in mice and human primary GEnCs, respectively, revealed alterations in the expression of genes crucial for maintaining the integrity of the GFB. Specifically, knockout/knockdown of ADGRF5 significantly downregulated type IV collagens (Col4a3 and Col4a4) that comprise the GFB and influence GFB permselectivity. In addition, Krüppel-like factor 2 (KLF2), a mechanosensitive transcription factor that regulates endothelial cell functions, was found to be upregulated.
Taken together, their findings highlight the critical functions of ADGRF5 in maintaining the integrity of GFB. Emphasizing the potential impact of the research work, Dr. Nakamura says, "This study reveals a novel mechanism that maintains the GFB. Insights into the role of ADGRF5 aids the understanding of glomerular disorders and significantly contributes to the advancement of future research."
Unlocking the novel functions of the ADGRF5 receptor holds promise for pioneering therapeutic breakthroughs in treating glomerular filtration barrier dysfunctions, notably proteinuria.
- Reference
| Authors : | Miki Nagase1,2, Hikaru Ando3, Yoshiaki Beppu3, Hidetake Kurihara2,4, Souta Oki3, Fumimasa Kubo3, Kazuki Yamamoto3, Takashi Nagase5, Shinya Kaname6, Yoshihiro Akimoto7, Hiroshi Fukuhara8, Tatsuo Sakai2, Shigehisa Hirose3, and Nobuhiro Nakamura3 |
|---|---|
| Title : | Glomerular Endothelial Cell Receptor Adhesion G-Protein-Coupled Receptor F5 and the Integrity of the Glomerular Filtration Barrier |
| Journal : | Journal of the American Society of Nephrology |
| DOI : | 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000427 |
| Affiliations : | 1Department of Anatomy, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Japan 2Department of Anatomy and Life Structure, Juntendo University School of Medicine, Japan 3School of Life Science and Technology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 4Department of Physical Therapy, Faculty of Health Science, Aino University, Japan 5Kunitachi Aoyagien Tachikawa Geriatric Health Services Facility, Japan 6Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Japan 7Department of Microscopic Anatomy, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Japan 8Department of Urology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Japan |
| * Corresponding authors' emails: | nnakamur@bio.titech.ac.jp and mnagase@ks.kyorin-u.ac.jp |
- Nobuhiro Nakamura | Researcher Finder - Tokyo Tech STAR Search
- NAKAMURA Lab
- [Labs spotlight] Nobuhiro Nakamura Laboratory | Life Science and Technology News
- Department of Life Science and Technology, School of Life Science and Technology
- Kyorin University
- Latest Research News
School of Life Science and Technology
—Unravel the Complex and Diverse Phenomena of Life—
Information on School of Life Science and Technology inaugurated in April 2016
Further Information
Associate Professor Nobuhiro Nakamura
School of Life Science and Technology, Tokyo Institute of Technology
E-mail nnakamur@bio.titech.ac.jp