Materials Science and Engineering News
Development of highly active and stable ammonia synthesis catalyst under low temperatures
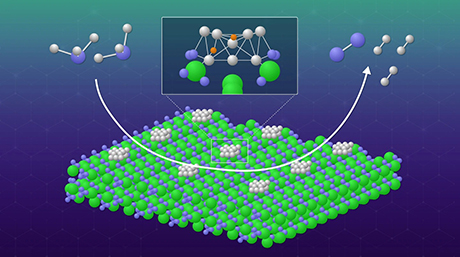
Profs. Hosono, Hara, Kitano, Abe and Dr. Inoue found that ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on calcium amide (Ca(NH2)2) function as an efficient catalyst for ammonia synthesis at 300 ℃ and the catalytic activity is more than 10 times higher than that of the highest performance Ru catalysts reported so far. In addition, 3% Ba-doped Ca(NH2)2 supported Ru catalyst exhibited excellent stability during reaction for 700 h (almost 1 month).
Ammonia is mainly consumed as a fertilizer in crop production and has attracted much attention as a promising candidate for a hydrogen carrier. The present findings will significantly promote the development of the energy-saving processes of ammonia synthesis. Commonly, most of Ru catalysts are supported on metal oxides or carbon materials. In the present catalyst, flat-shaped Ru nanoparticles with a uniform size distribution are distinctly anchored on the surface of Ca(NH2)2 by strong Ru-N interaction. As a result, Ru-loaded Ca(NH2)2 exhibits high catalytic performance and long term stability for ammonia synthesis under low reaction temperatures.
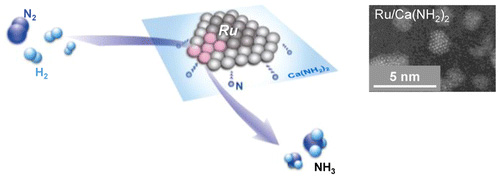
Figure. Conceptual diagram of ammonia synthesis activity at low temperature micro-pressure conditions using a catalyst with a fixed ruthenium on calcium amide (left). Electron microscopic image of the catalyst fixed ruthenium calcium amide (right).
Acknowledgment
R&D Project "Materials Science and Application of Electrides", this work was supported by a fund from Accelerated Innovation Research Initiative Turning Top Science and Ideas into High-Impact Values (ACCEL) of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST). A portion of this work was supported by a Kakenhi Grant-in-Aid (No. 15H04183) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Reference
| Authors: | Yasunori Inoue1, Masaaki Kitano2, Kazuhisa Kishida2, Hitoshi Abe3, 4, 5, Yasuhiro Niwa3, Masato Sasase2, Yusuke Fujita1, Hiroki Ishikawa1, Toshiharu Yokoyama2, Michikazu Hara1, 5, 6*, Hideo Hosono2, 5, 6* |
|---|---|
| Title of original paper: | Efficient and Stable Ammonia Synthesis by Self-Organized Flat Ru Nanoparticles on Calcium Amide |
| Journal: | ACS Catalysis, 6, 7577-7584 (2016) |
| DOI : | 10.1021/acscatal.6b01940 |
| Affiliations : | 1Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology 2Materials Research Center for Element Strategy, Tokyo Institute of Technology 3High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, KEK 4Department of Materials Structure Science, School of High Energy Accelerator Science, SOKENDAI, The Graduate University for Advanced Studies 5ACCEL, Japan Science and Technology Agency 6Laboratory for Materials and Structures, Tokyo Institute of Technology |
- FACES: Tokyo Tech Researchers, Issue 16 - Hideo Hosono, Part 1
- FACES: Tokyo Tech Researchers, Issue 16 - Hideo Hosono, Part 2
- Professor Hosono receives 2016 Japan Prize, gives commemorative lecture | Materials Science and Engineering News
- Finding new controlling method for properties of glass | Materials Science and Engineering News
- AGC starts mass-production of sputter target of C12A7 electride created by Tokyo Tech | Tokyo Tech News
- Hosono-Kamiya Laboratory
- Hara-Kamata Laboratory
- Researcher Profile | Tokyo Tech STAR Search - Hideo Hosono
- Researcher Profile | Tokyo Tech STAR Search - Michikazu Hara
- Researcher Profile | Tokyo Tech STAR Search - Masaaki Kitano
- Researcher Profile | Tokyo Tech STAR Search - Yasunori Inoue
- Materials research Center for Element Strategy
- Laboratory for Materials and Structures, Institute of Innovative Research
- Institute of Innovative Research
- High Energy Accelerator Research Organization(KEK)
- School of High Energy Accelerator Science, SOKENDAI, The Graduate University for Advanced Studies
- ACCEL, Japan Science and Technology Agency
- Latest Research News
Further information
Professor Hideo Hosono
Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Director, Materials Research Center for Element Strategy, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Email hosono@msl.titech.ac.jp
Tel +81-45-924-5009
About Program
Daichi Terashita
ACCEL Group, Department of Innovation Research, JST
Email suishinf@jst.go.jp