Life Science and Technology News
【Labs spotlight】 Kano Laboratory
Development of novel cell editing systems
The Department has a variety of laboratories for Life Science and Technology, in which cutting-edge innovative research is being undertaken not only in basic science and engineering but also in the areas of medicine, pharmacy, agriculture, and multidisciplinary sciences.
This "Spotlight" series features a laboratory from the Department and introduces you to the laboratory's research projects and outcomes. This time we focus on Kano Laboratory.

Areas of Supervision
Primary/Life Science and Technology
Associate Professor Fumi Kano![]()
*Professor Kano was promoted from Associate Professor to Professor on April 1, 2024.
| Degree | PhD 2002, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University |
|---|---|
| Areas of Research | Cellular Biology, Cell Engineering |
| Keywords | Cell Editing, Human iPS Cells, Semi-intact cells, Cell-resealing, Image Analysis |
| Website | Kano Laboratory |
Research interest
Cell-editing technology based on cell-resealing technique
Kano lab is devoted to the development of "Cell-editing technology" to design functions and fate of cells by using "cell-resealing technique", which enables the free introduction of various molecules such as proteins, nucleotides, membrane-impermeable small molecules, etc. into cells (see figure). We also do research into integrating the analysis of cellular images obtained by microscopic observation with mathematical analysis to identify the key molecules for the various biological processes.
Current research directions of Kano lab include
- 1.Development of human iPS cell-editing system for cell therapy
- 2.Frontier cellular image analysis to study biomolecular networks in disease cells
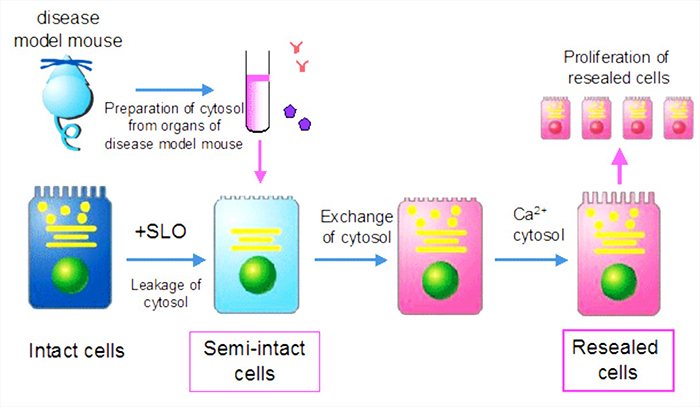
Scheme of cell-resealing technique
Research findings
Selected publications
- [1] Matsuto, M., Kano, F., Murata, M. (2015) Reconstitution of the targeting of Rab6A to the Golgi apparatus in semi-intact HeLa cells: A role of BICD2 in stabilizing Rab6A on Golgi membranes and a concerted role of Rab6A/BICD2 interactions in Golgi-to-ER retrograde transport. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 1853 (10): 2592-2609. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.05.005 .
- [2] Taguchi, Y., Imaoka, K., Kataoka, M., Uda, A., Nakatsu, D., Horii-Okazaki, S., Kunishige, R., Kano, F., Murata, M. (2015) Yip1A, a Novel Host Factor for the Activation of the IRE1 Pathway of the Unfolded Protein Response during Brucella infection. PLOS Pathogens. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004747 .
- [3] Nakatsu, D., Horiuchi, Y., Kano, F., Noguchi, Y., Sugawara, T., Takamoto, I., Kubota, N., Kadowaki, T., Murata, M. (2015) L-cysteine reversibly inhibits glucose-induced biphasic insulin secretion and ATP production by inactivating PKM2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 112 (10): E1067-1076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417197112.
- [4] Sugawara, T., Kano, F., Murata, M. (2014) Rab2A is a pivotal switch protein that promotes either secretion or ER-associated degradation of (pro)insulin in insulin-secreting cells. Scientific Reports. 4. Article number: 6952. doi:10.1038/srep06952.
- [5] Nakatsu, D., Kano, F., Taguchi, Y., Sugawara, T., Nishizono, T., Nishikawa, K., Oda, Y., Furuse, M., Murata, M. (2014) JNK1/2-dependent phosphorylation of angulin-1/LSR is required for the exclusive localization of angulin-1/LSR and tricellulin at tricellular contacts in EpH4 epithelial sheet. Genes Cells. 19 (7): 565-581. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12158.
- [6] Fujiki, K., Shinoda, A., Kano, F., Sato, R., Shirahige, K., Murata, M. (2013) PPARγ-induced PARylation promotes local DNA demethylation by production of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nature Communications. 4. Article number: 2262. doi:10.1038/ncomms3262.
- [7] Kano, F., Murata, M. (2013) The Semi-Intact Cell System and Methods for Cell Resealing: a Novel Systems Biology Tool to Elucidate Protein Networks with Spatio-Templioral Information. Advances in Systems Biology. 2(1): 6-14.
- [8] Murata, M., Kano, F. (2012) Semi-intact cell system: Application to the nalysis of membrane trafficking beween the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus and of cell cycle-dependent changes in the morphology of these organelles. in Crosstalk and Integration of Membrane Trafficking Pathways. (Weigert, R. ed.) INTECH (ISBN 978-953-51-0515-2)
- [9] Kano, F., Nakatsu, D., Noguchi, Y., Yamamoto, A., Murata, M. (2012) A Resealed-Cell System for Analyzing Pathogenic Intracellular Events: Perturbation of Endocytic Pathways under Diabetic Conditions. PLoS ONE. 7(8):e44127.
- [10] Kano F, Arai T, Matsuto M, Hayashi H, Sato M, and Murata M. (2011). Hydrogen peroxide depletes phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate from endosomes in a p38 MAPK-dependent manner and perturbs endocytosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. (Molecular Cell Research), 1813(5):784-801.
Contact
Associate Professor Fumi Kano
Room 609, S2 building, Suzukakedai campus
E-mail : kano.f.aa@m.titech.ac.jp
*Find more about the lab and the latest activities at the lab site![]() .
.
*May 1, 2025:Some of the content has been updated with the latest information.